Understanding sparse matrix: A key concept in machine learning
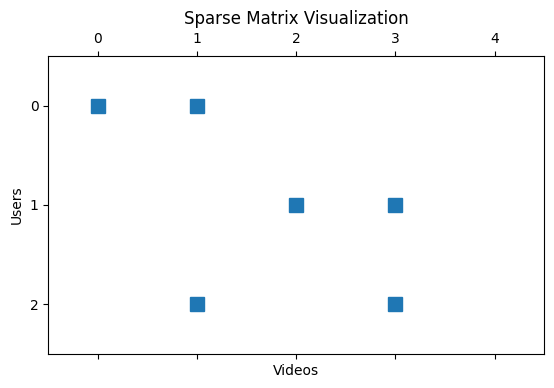
Sparse matrix is a common occurrence in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer graphics, where most or all matrix elements are zero. Example: user feedback dataset of YouTube recommendation system, with millions of variables about likes, dislikes, watches, and the like. Considering that most users didn’t choose any, only a small percentage of the matrix are non-zero elements representing explicit feedback.
Thulasi
Jan 6, 2026 |
10 mins

Challenges of sparse data in machine learning
Let’s continue with the above example. You need to train the YouTube recommendation system using user feedback, predicting if the suggestion is relevant or not. Dealing with a feedback matrix like this, with unobserved (or missing) data, would require any of the following ways.
1. Explicit Feedback: Direct signals from the user, like ratings or likes.
2. Implicit Feedback: Indirect signals such as watch time or click-through rate.
3. Explicit + implicit: Combining both explicit and implicit feedback to get a comprehensive view of user preferences.
The challenge with sparse matrices is that it leads to model bias, leading to predictions that are close to zero or neutral, which are undesirable. Such bias prevents the model from generalizing well to new, unseen ⟨user, video⟩ pairs, limiting its ability to make accurate recommendations.
Sparsity in feature spaces
Not only feedback systems, sparse matrices also occur while dealing with high-dimensional feature spaces in machine learning models. Consider a scenario where you have thousands of features, but most of them have values as zero for any given data point. This is common in natural language processing (where word vectors are often sparse), categorical variables with many unique values (e.g., one-hot encoding), and representing network connections (edges in a graph).
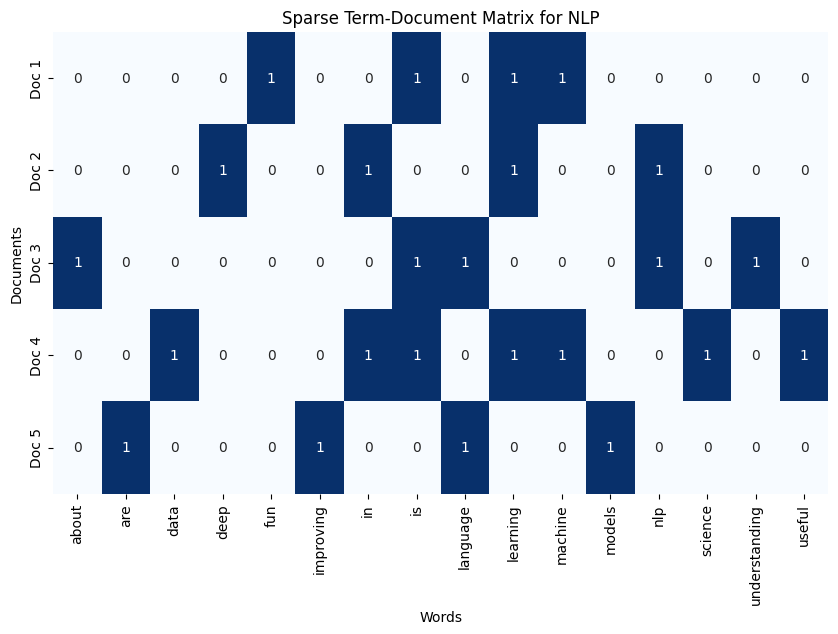
Consider the following example, with sentences (documents) containing overlapping words. Let’s try generating a Term-Document Matrix based on these documents. In the generated matrix, every row should stand for a document and every column for a word, with the values indicating the frequency of the word in the document.
# Example documents documents = [ "machine learning is fun", "deep learning in nlp", "nlp is about understanding language", "machine learning is useful in data science", "language models are improving" ]
Overcoming Sparsity in Machine Learning
Sparse situations are not unique to machine learning—they happen in real life too! Imagine traveling with a phone battery about to die, or having limited money during a festive season. We prioritize, reduce usage, and reuse wherever possible to make resources last longer to manage these situations.
Similarly, overcoming sparsity in machine learning involves strategies that help us make the most of the limited data we have. We employ techniques that prioritize the important bits of data, reduce unnecessary complexity, and reuse patterns to fill in gaps.
A key part of this process connects to what is feature engineering in data science—the practice of transforming raw inputs into meaningful features that models can actually learn from. By engineering better features, we can extract deeper insights from sparse matrices, enhance model accuracy, and ultimately solve the business problem more efficiently.
Let’s explore some methods that help us deal with sparse matrix and turn limited data into stronger predictions.
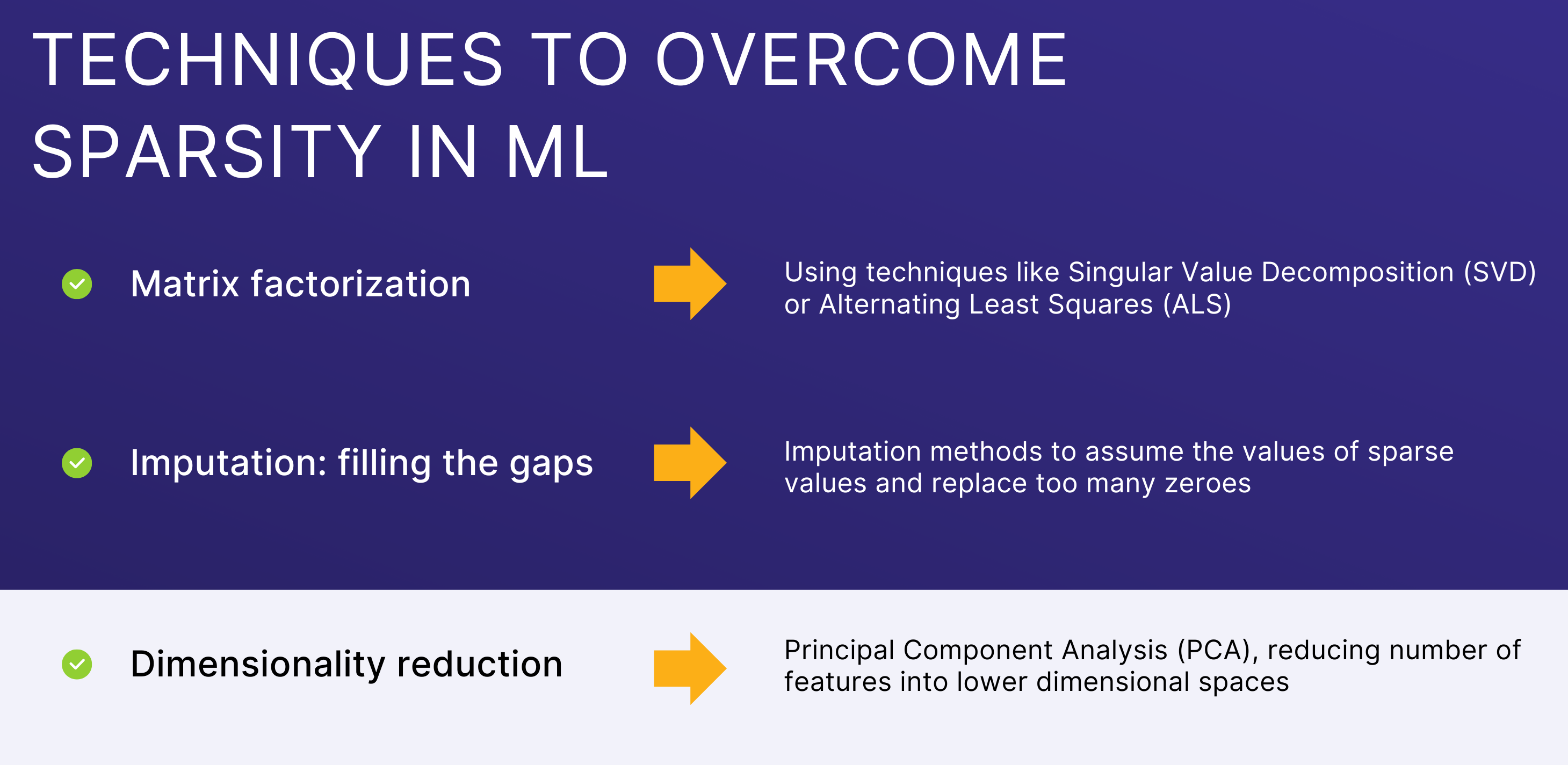
1. Matrix factorization
Using matrix factorization is like dealing with a dying battery by dimming the screen, turning off unnecessary apps, and focusing on what's essential. Matrix factorization techniques like Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) or Alternating Least Squares (ALS) break down the sparse matrix into smaller, denser matrices. These reconstructed matrices uncover latent factors, or hidden patterns, that help explain user preferences even when explicit feedback is missing. This way, recommendation systems can still make accurate feedback with uncovered patterns, even with sparse feedback.
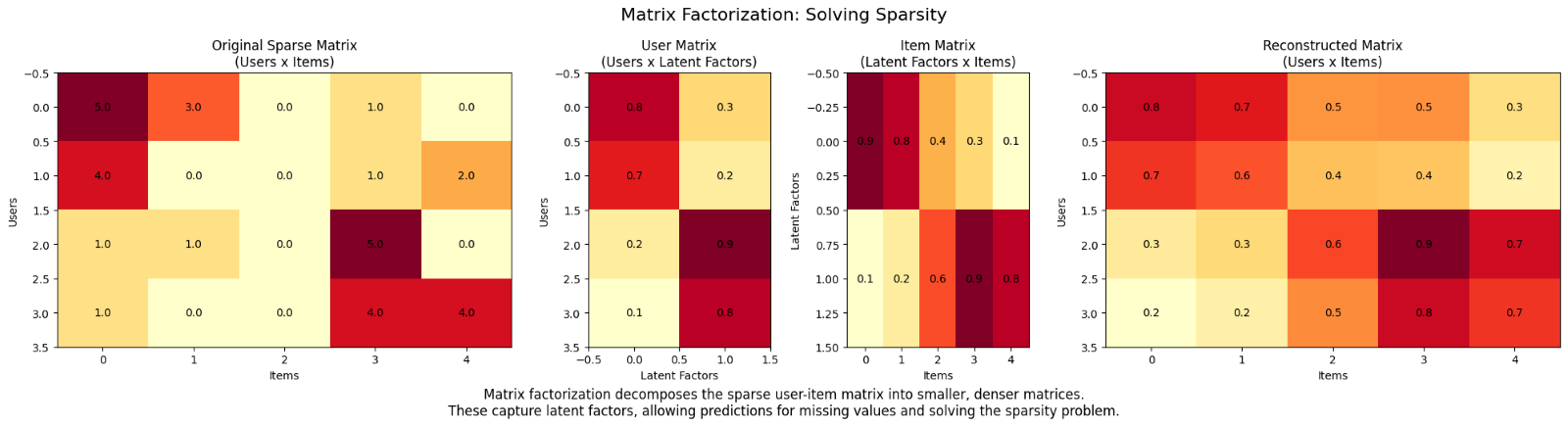
Original matrix sparsity: 40% Reconstructed matrix sparsity: 0%
2. Imputation: filling the gaps
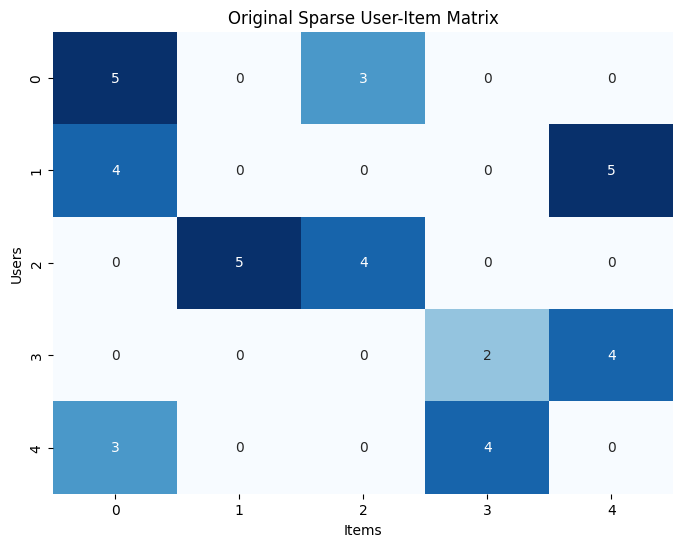
Imagine being low on ketch-up and adding water or other sauces to make it last. Similarly, in ML, we use imputation methods to fill in missing data intelligently. Imputation methods estimate the missing values in a sparse matrix by using the available data. This reduces the number of zeroes, enabling recommendation or customer behavior models to learn more effectively and generate accurate predictions.
For example, in collaborative filtering, we use similarities between users or items to infer the missing feedback.
3. Dimensionality reduction: simplifying the problem
Consider the analogy of spending frugally and prioritizing essentials when you are low on money. That’s how dimensionality reduction works, simplifying learning for ML models with sparse matrices. It uses techniques like Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce the number of features by transforming them into a lower-dimensional space. This helps make the data denser and removes redundant or irrelevant features.
With reduced feature spaces, the model focuses only on core factors directly that drive accurate predictions. Hence, dimensionality reduction is great for high-dimensional datasets like text analysis or large-scale customer segmentation.
# Let’s generate some sparse data using this code import numpy as np np.random.seed(42) n_samples, n_features = 300, 100 X = np.zeros((n_samples, n_features)) for i in range(n_samples): non_zero_indices = np.random.choice(n_features, 5, replace=False) X[i, non_zero_indices] = np.random.randn(5)
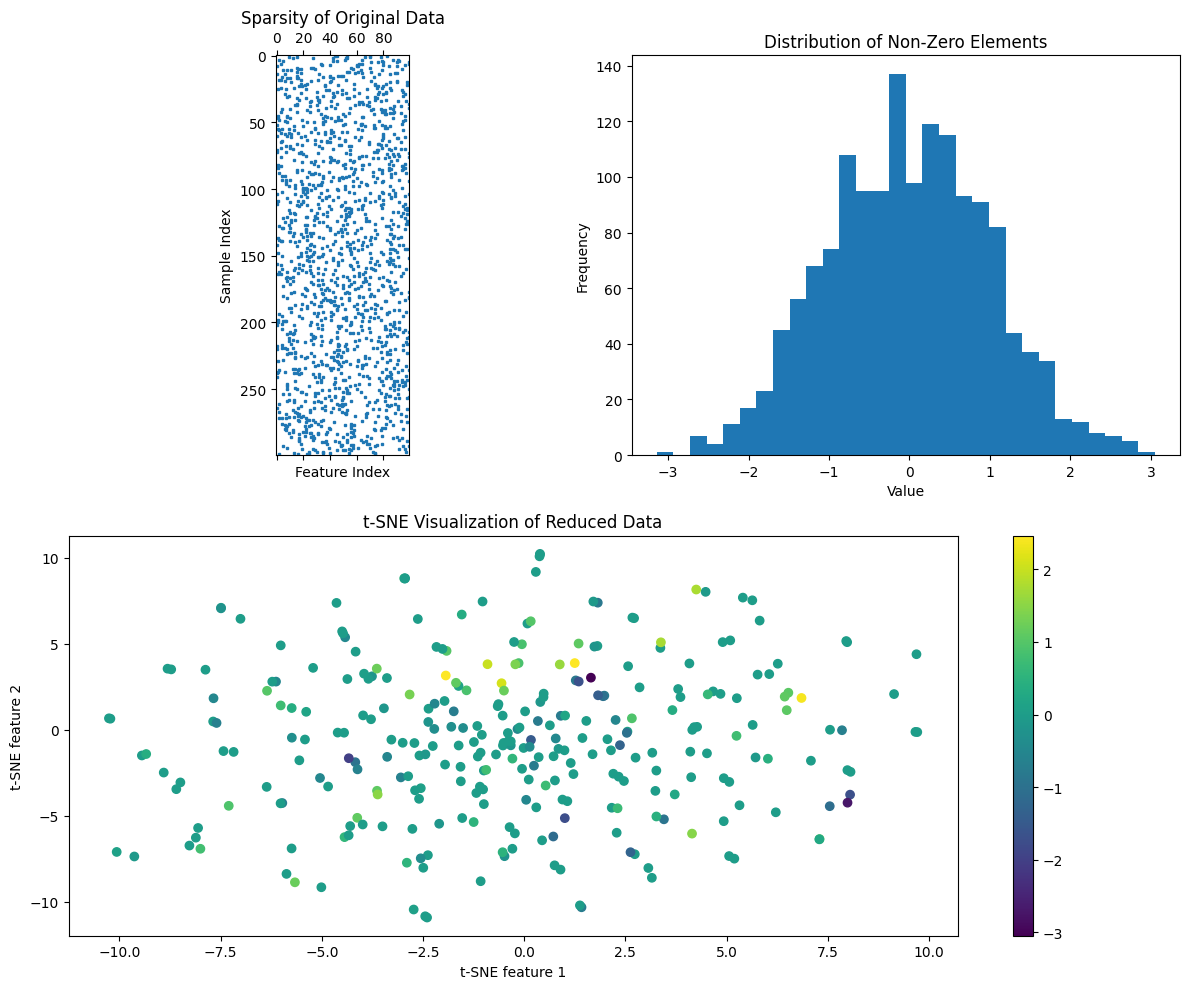
Sparsity of the data: 95.00%
Original dimensions: (300, 100)
Reduced dimensions: (300, 2)
4. Deep learning with embeddings
How about stretching limited money by finding good deals? Deep learning embedding works this way, learning compact, efficient representations. Embeddings are dense, lower-dimensional representations of high-dimensional sparse inputs. In recommendation systems, embedding layers represent users and items in such a way that similar users and items are closer together in the learned space.
Embeddings allow the model to capture complex relationships, even when the input matrix is sparse. This technique is particularly useful in NLP tasks and recommendation engines, where sparsity is a major issue. It helps the model generalize well and improves recommendations.
# Let's create a synthetic sparse user-item interaction matrix import numpy as np user_item_matrix = np.array([ [1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 0], [1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1] ])
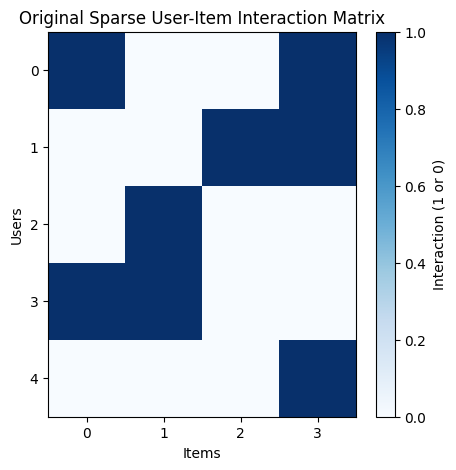
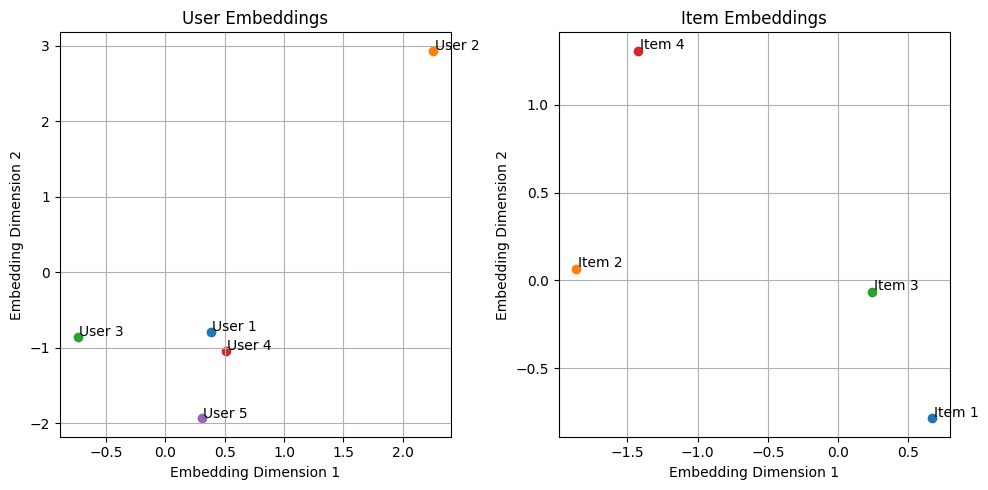
Final thoughts: from sparse data to business impact
By applying these techniques, we can transform sparse data into actionable insights. For example, in a recommendation system like that of YouTube, matrix factorization or embeddings helps the system recommend relevant videos, even with limited explicit feedback. Similarly, in customer analytics, imputation and dimensionality reduction allow us to better understand user behavior, improving customer targeting and personalization. Sparsity is a challenge, but with the right strategies and support from good data consulting companies, we can overcome it and unlock valuable patterns in the data, leading to better machine learning models and ultimately, more informed business decisions.
Unify your data. Strengthen your pipelines. Do it with expert data integration engineering services.
Frequently asked questions
1. Which ML algorithms benefit from sparse matrices?
Algorithms like linear & logistic regression, Linear SVMs, Naive Bayes (text, event data), Matrix factorization (recommendation systems), tree-based models, and neural networks with embeddings benefit from sparse matrices. These algorithms and models can use sparse matrices for faster computation, lower memory usage, and better generalization in high-dimensional spaces.
2. How to deal with sparse data in machine learning?
There are multiple strategies for dealing with sparse data in machine learning, like feature selection, regularization, using sparse-aware data structures, and avoiding native imputations.
3. How to optimize ML models for sparse input?
Optimizing ML models for sparse inputs happen through three levels: data, model, and system level. Here are some optimization strategies at all three levels.
Data level
Drop extremely rare features
Bucket long-tail categories
Use log-scaling for count features
Model level
Prefer linear or shallow models first
Use sparse-optimized solvers
Add regularization early
For deep learning, embed first—then model
System level
Use sparse matrix libraries
Avoid dense conversions in pipelines
Monitor memory, not just accuracy