Microsoft Fabric vs Snowflake: Know the differences and features
Hear from our data engineering team as they share everything about Microsoft Fabric vs Snowflake, similar features and differences, etc.. Dive deep into details on how both tools can work together and finally hear the verdict on which tool is suitable for what companies. This blog is for you if you are planning to select the right cloud data platform.
Suresh
Jan 1, 2026 |
15 mins
What is Microsoft Fabric?
Microsoft Fabric is a comprehensive data platform to connect various data workloads from pipelines to storage to visualization to AI/ML. It helps you manage centrally governed data within your organization, while compartmentalizing data for each division, functional area, or team. For these reasons, Microsoft Fabric is great for enterprises and growing organizations that need unified analytics, integration, and storage solutions. The highlight of the tool is not just Microsoft Fabric components but also OneLake, which is the unified storage part of the tool.
Pros of Microsoft Fabric
Simplified SaaS environment that’s easy to use for all kinds of data users.
Real-time intelligence enabled, to obtain business insights as fresh as possible.
Smooth collaboration across teams where everyone can work on their data workload with a unified version of data.
Co-pilot to automate routine tasks, create quick reports, and build auto-models.
Use the newly released capability, AI skills in Microsoft Fabric to design and customize Q&A systems (assistants) within Fabric.
High performance and low latency as Microsoft availability centers are present all over the world.
MS Purview to apply unified data governance, data security, and compliance policies across the organization.
Stress-free billing and payment as you get multiple experiences under one billing.
Learn more: Benefits of Microsoft Fabric
Cons of Microsoft Fabric
Many components like Power BI, Data Factory, etc., are pre-existing in the market packaged into one tool, Fabric.
While the platform is unified with many components and features, there might be a few limitations on customizing certain features compared to the stand-alone counterparts.
What is Snowflake?
Snowflake is a modern, cloud-based data warehousing platform. It’s great for businesses that look for a flexible, high-performance, and scalable platform for analytics and storage with tightly decoupled compute and storage. Though Snowflake started as a traditional data warehousing platform, it has evolved into much more than that with extended capabilities and integrations. For example, it can,
Function as a data lake, handling raw, structured, and unstructured data.
Data engineering tasks like integration, ETL, transformation, along with an easy-to-use SQL reporting interface.
Data sharing and marketplace for collaborative working and third-party data access.
AI and machine learning - ability to write and execute ML codes in Python, R, etc. within Snowflake, closer to where your data resides.
Integration with visualization tools like Power BI, Tableau, Qlik, etc.
Pros of Snowflake
Elastic compute - can scale up and down to suit your business requirements.
Can work across all cloud providers like AWS, GCP, etc, supporting businesses to go for multi-cloud strategy.
Multiple users can work on the data without having to move or copy the data.
Cons of Snowflake
Steep learning curve for those who are not familiar with cloud-based data warehousing solutions.
Since Snowflake is a cloud-agnostic platform, it’s not suitable for on-premises systems. Vendor lock-in issues may arise, especially for companies with hybrid assets.
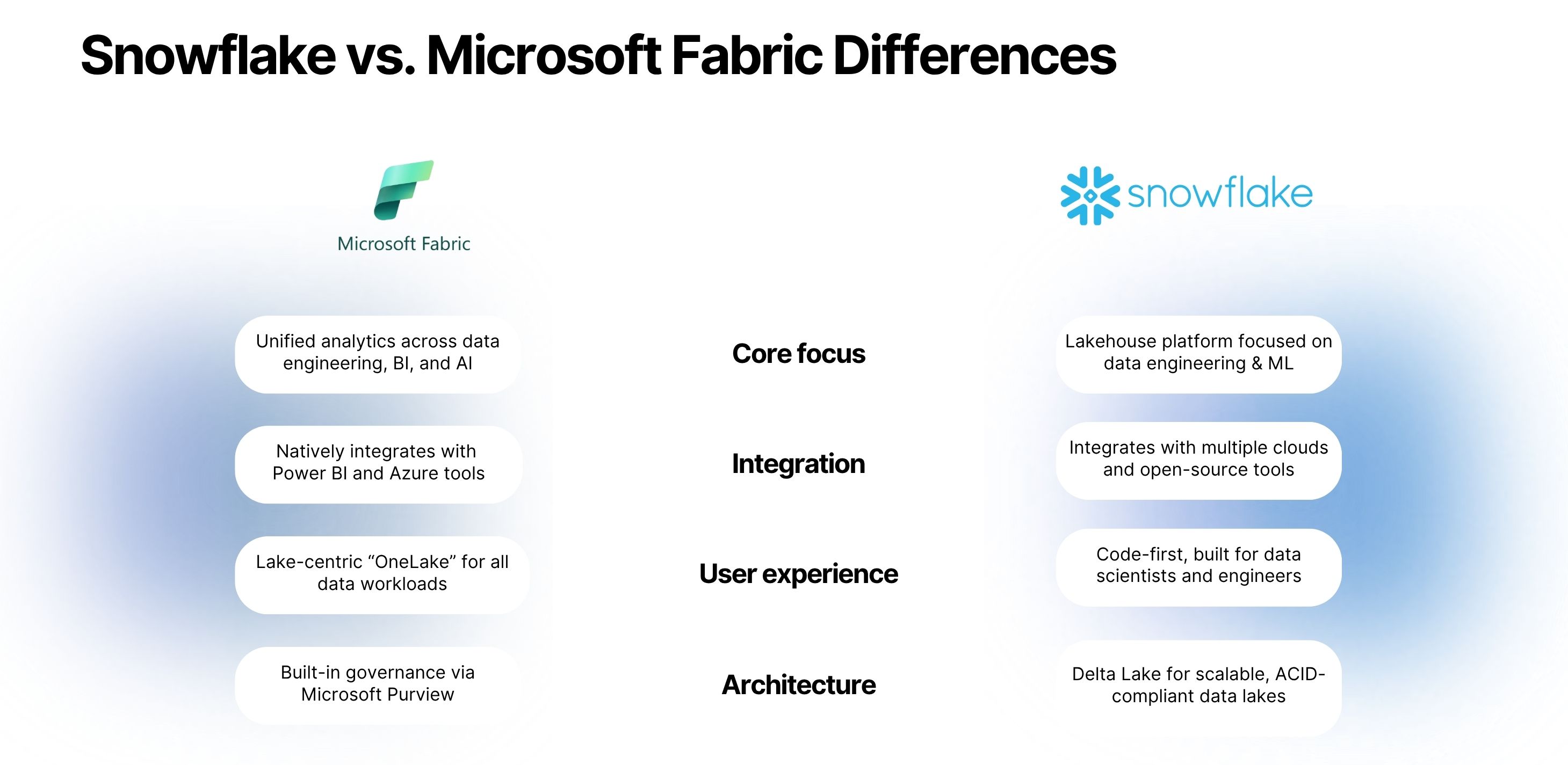
Difference between Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake
Factors | Microsoft Fabric | Snowflake |
Performance | Microsoft Fabric is faster in performance as data resides within OneLake and travels in shorter pipelines. It doesn’t duplicate data. So, for a Microsoft-centric data environment, speed and reliability will be satisfactory for all data workloads. However, it might take some tuning and optimizing to achieve the desired performance for complex tasks. | Like Fabric, Snowflake is an equally powerful and high-performance platform for data analytics and other purposes. It separates storage from the compute. Thus, multiple clusters can run parallel without affecting one another. This very reason also improves query performance, allowing Snowflake to spin resources to cater to multiple queries simultaneously. Its columnar storage format is also one reason for its fast query execution. |
Pricing | Comes with pay-as-you-go pricing options charging you based on the consumed compute, storage, and processing. If your company has predictable workloads, you could reserve instances and get up to 40% discount. If you want a capacity-based billing with a broader range of services at a unified, cost-effective price, Microsoft Fabric will suit your needs. | Has a pay-as-you-go model, but it charges for storage and compute size (for time when you execute queries) separately. Similar to Fabric and Azure services, Snowflake has pre-purchase capacity plans too. If you prefer a more transparent billing nature with unlimited compute capabilities, Snowflake can offer that. |
Architecture | Microsoft comprises six major components united by the OneLake data storage and unified governance. The six components include, Data factory: this can help you build pipelines and connect data from external sources with no-code and low-code connectors. Data engineering: For data warehousing, engineering, and Notebook access. Real-time intelligence: Convert real-time streaming data into business insights. Visualization: Build reports and visualization for business users. Azure Synapse: For compute and processing, comes with Spark Pools, SQL pools, and Synapse SQL. Data science: Azure ML to build and deploy models and AI solutions. The more number of components here make Fabric more than a data warehousing and analytics platform, which can work throughout the data lifecycle. | Snowflake is known for its separation of compute and storage. Its architecture contains three zones. Storage layer: For encrypted storage of data in formats like JSON, Avro, or Parquet. Compute layer: Virtual warehouses or a cluster of compute nodes. Cloud services layer: For query processing, metadata management, security and governance, and ACID transactions. Snowflake’s architecture makes it a suitable single or multi-cloud-native platform that can work with all providers like Google, Microsoft, or AWS. |
Integration | Fabric wins here with seamless integration possibilities within and beyond Microsoft stack. It integrates with Microsoft 365, Azure services, and other third-party BI tools and data sources. It has a data factory if you want to utilize no-code connectors and REST API for custom integration. Unlike Snowflake, you could also integrate and create a copy of on-premise data sources into Fabric as well. | Being a cloud-agnostic platform, Snowflake connects with all cloud data storage sources. Snowflake uses built-in and third-party Integrations to facilitate ETL and other connections with databases, API services, SaaS apps, and streaming platforms. While Snowflake has an extensive partner ecosystem and connects with all kinds of data transformation, ingestion, and ML tools, Fabric wins, as it offers the most within one ecosystem. |
Storage and support | Data storage of Microsoft Fabric is taken care of by OneLake, an integrated storage built on top of ADLS Gen 2 to support unstructured/semi-structured data. Also has Synapse analytics for structured warehouse storage. Requires a bit of manual configuration if you want to manage storage across Azure services. Fabric takes the lead when it comes to high-volume storage and warehousing. | Data storage here is a centralized cloud storage that’s separated from its compute resources. Supports both structured and semi-structured forms of data. Its notable feature includes automatic data partitioning, which makes it much simpler to find data while querying. It also comes with unlimited scalability and doesn’t require careful configuration unlike Fabric for it separates compute from storage. |
Security and compliance | Built on top of Azure, Microsoft Fabric inherits its robust security and compliance features to protect your sensitive data. Uses Azure virtual networks to protect your data and isolate them. Its compliance list is strong and more comprehensive than Snowflake with HIPPA, SOC 1, 2, 3, GDPR, etc. For governance, it comes with a built-in tool called Purview which can do sensitive information classification, data lineage, and more. | While Snowflake has equally strong governance features like role based user access, metadata management, etc, it doesn’t have an inbuilt tool like Purview. Other than that, its security features and compliance certifications are equally strong as that of Fabric. Another difference between Snowflake and Microsoft Fabric is the former offers security features across multiple cloud providers - Google, AWS, etc. |
Reporting | Microsoft Fabric has its built-in visualization tool, Power BI. You can use it to build interactive dashboards and reports in no time. Power BI within fabric is much faster than it working standalone, as ingestion, transformation, and storage happens within Fabric here. Layered with Copilot, it allows you to interact better with your data and offer advanced insights and summaries. Fabric’s integration with Microsoft 365 extends these benefits further, allowing easy sharing and collaboration between teams. | Snowflake doesn’t have an inbuilt visualization tool like Microsoft Fabric. But it can connect with other BI tools like Qlik, Tableau, Power BI, Looker, etc. It also facilitates data sharing in other ways. Secure data sharing with external parties Advanced analytics and SQL-based reporting, which can be connected to BI tools to build reports. Storing query results to promote faster delivery of data for complex queries. Even with these data sharing abilities, Microsoft Fabric wins in this case, as it comes with the visualization tool. |
Can Microsoft Fabric connect to Snowflake?
Yes. Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake integration is possible. If you are using Snowflake for data warehousing, you could very well connect/mirror the data in Fabric for visualization or data science. There are two possible reasons why you should connect Snowflake to Microsoft Fabric.
Run visualization using Power BI on data from Snowflake
Use ADF to ingest and transform data from Snowflake to other Azure services for further analysis or processing.
Manage operations seamlessly in a multi-cloud environment and run ML/AI solutions with data from Snowflake.
Steps to connect Snowflake to Microsoft Power BI
You could use either import’ mode or ‘direct query’ mode available in Power BI to connect Snowflake to Power BI.
Open Power BI and go to ‘Get data’.
From sources, select ‘Snowflake’.
Enter details like server name, database, schema, etc., and enter your password.
Choose either ‘import’ or ‘direct query’ mode.
Your data is imported from Snowflake into Power BI now. You can start building reports now.
What is Snowflake in Azure?
Snowflake in Azure means the integration of Snowflake with Azure ecosystem. By connecting Snowflake with ADF, Synapse analytics, or machine learning, you can enjoy the following benefits.
Azure Data Factory: For orchestration of pipelines between Snowflake and other Azure services.
Azure Synapse Analytics: This is to split high volume data processing workloads into two, one being handled by Snowflake and the other by Synapse analytics.
Check out our Azure synapse analytics vs Microsoft Fabric comparison blog, where we have covered more information on this.
Azure AI and ML: Use data from Snowflake to power advanced ML and AI workflows. Snowflake and Azure integration give you the best of both worlds, allowing smooth multi-tier data management, hybrid analytics, and real-time reporting. Is Microsoft Fabric like Snowflake?
Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake are both data platforms with a few common traits. But Microsoft Fabric is not like Snowflake, which is only a cloud-based data storage and processing platform.
Microsoft Fabric is much more comprehensive than Snowflake with many in-built components, so everything from ingestion to visualization happens in one ecosystem. Whereas, Snowflake, despite its great virtual private networks, advanced SQL, and limitless compute and scaling, isn’t strong with native integrations and a broad set of services.
This is why Microsoft Fabric is more like an end-to-end analytics system where Snowflake is more of a managed cloud platform with storage, compute, and processing.
Final thoughts
The verdict of Microsoft Fabric vs. Snowflake is that both are great platforms on their own, each with unique strengths and advantages. It depends on your business problems, data challenges, and your existing infrastructure. If you have on-prem, cloud, or hybrid data sources, you could use MS Fabric, which supports all. If talking to a modern data architecture engineering services team can help, fix an introductory call with us & decide the best data analytics solution for your company.
FAQs
1. Should I migrate my snowflake to microsoft fabric?
You should migrate to Microsoft Fabric if you are already using one or many of the tools listed here: Power BI, ADF, Notebooks, cloud data warehouses, and governance tools. While Snowflake looks like a very great choice for data warehouse, if your data tool stack looks scattered like the below, migrating to Power BI comes with great set of benefits.
Snowflake for storage
ADF / Fivetran / dbt for ingestion and pipelines
Power BI or Tableau for visualization
Databricks or notebooks for ML and experimentation
Separate governance & catalog tools
Especially if your organization is already reliant on Microsoft ecosystems or Power BI, moving to Fabric will reduce the BI friction your teams experience, stitch everything together, and enjoy more predictable billing (Fabric has capacity-based model) where teams can experiment without cost anxiety.
2. How to choose between Snowflake and Microsoft Fabric for your business?
Between Snowflake and Microsoft Fabric, you have to choose Snowflake if you manage SQL-based workflows, want a decoupled architecture where multiple warehouses can run parallel, and integrate well with modern data tools. However, you can choose Microsoft Fabric over Snowflake, if you need seamless connectivity between data ingestion and BI layer. Any company wanting an end-to-end analytics solution would choose Fabric over Snowflake for its unified governance and security, all-in-one platform capabilities (ingestion, transformation, storage, BI, ML, governance), and strong alignment with Microsoft.
3. Microsoft Fabric vs Snowflake for data engineering
Both Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake are strong for data engineering, but they serve different needs.
Snowflake offers greater engineering depth and flexibility. It integrates well with best-in-class tools such as Airflow, dbt, Spark, and external CI/CD systems, making it ideal for mature ELT patterns, SQL-first transformations, and high-concurrency workloads. Teams that want fine-grained control over pipelines, performance tuning, and deployment workflows often prefer Snowflake.
Fabric focuses on end-to-end delivery. It combines ingestion, notebooks, transformations, storage, governance, and BI in one platform, reducing integration overhead and simplifying operations. It works especially well when Power BI is central and governance needs to be enforced consistently.
In practice, Snowflake suits teams prioritizing engineering control, while Fabric suits teams prioritizing simplicity and speed.

by Suresh
Suresh, the data architect at datakulture, is our senior solution architect and data engineering lead, who brings over 9 years of deep expertise in designing and delivering data warehouse and engineering solutions. He is also a Certified Fabric Analytics Engineer Associate, who plays a major role in making us one of the early adopters of Fabric. He writes in words whatever he delivers with precision to his clients, consistently voicing out trends and recent happenings in the data engineering sector.