Handling Streaming data in Power BI – From basics to results
I want to know how Power BI can support continuous, flowing, and dynamic data (basically streaming). For tracking website activity, monitoring IoT devices, or analyzing customer engagement in real time. Do you think the same way too? Our senior data engineer has written this blog, explaining streaming data capabilities of power BI.
Kannabiran
Dec 31, 2025 |
10 mins

What is streaming data in Power BI?
Imagine being able to see what’s happening in your business right now, not five minutes or five hours later. That’s what streaming data does.
Streaming data is information that’s continuously generated — from machines, apps, websites, or sensors — and flows in real time. Power BI can capture this nonstop stream and turn it instantly into live dashboards, so you can monitor what’s happening the very moment it happens.
Unlike static reports that refresh once or twice a day, Power BI’s streaming datasets update in seconds — giving you dashboards that move with your business.
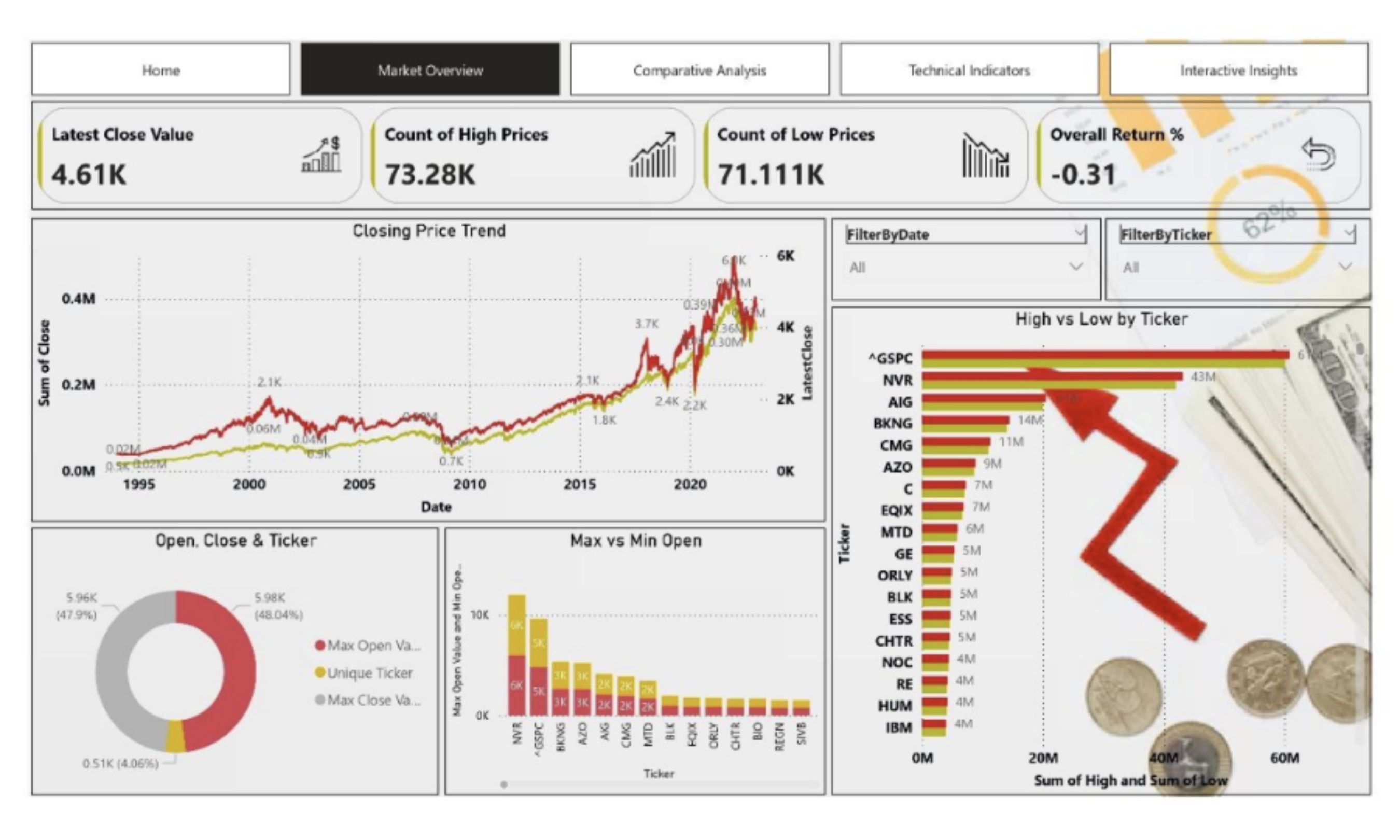
An example of streaming data being demonstrated effectively in Power BI is a stock market live update dashboard which helps with:
Latest Market KPIs: Cards showing the latest close value, overall return percentage, and counts of highs and lows.
Real-Time Trend Analysis: Line charts that update continuously to display closing price movements over time.
Comparative Insights: Bar charts comparing highs vs. lows by ticker, helping identify strong and weak performers at a glance.
Interactive Filtering: Users can drill down into specific tickers or dates instantly, enabling focused analysis on-demand.
Dynamic Alerts: Visual cues highlight sudden spikes or unusual market changes in real time
Such streaming data dashboards minimize the need for waiting for end-of-day reports, so decision-makers can be swift about their decisions and monitor fluctuations and spot emerging trends—an approach that can be applied to many industries beyond finance (retail, manufacturing, IoT, and more).
Examples of Streaming Data in Action
Smart Manufacturing: Track machine sensors live to catch faults before they cause downtime.
Retail & E-Commerce: Watch sales, orders, and inventory update second by second during a flash sale.
Cybersecurity: Get alerted the instant there’s unusual login activity or a spike in network traffic.
Finance: Follow stock prices and market indices as they change — no manual refresh required.
Customer Engagement: Monitor real-time social media mentions to respond instantly to customer trends.
Three approaches to process streaming data in Power BI
Power BI supports three main ways to bring real-time data into dashboards — depending on whether you need to store data, visualize it instantly, or handle massive, fast-moving streams.
1. Push Datasets
Push datasets are used when you need both real-time visibility and historical tracking. Data is sent (or “pushed”) into Power BI using APIs, and it’s stored for later analysis. That means you can view live updates now and still run long-term reports later.
Example: Tracking daily sales orders — you can see real-time KPIs for ongoing sales while analyzing weekly or monthly performance trends later.
Best for: Scenarios where you need live dashboards today and historical insights tomorrow.
2. Streaming Datasets
Streaming datasets are all about immediacy. Data flows directly into Power BI visuals as it arrives — without being stored. This is ideal when only the latest data matters, and you don’t need to analyze historical records.
Example: Monitoring server uptime, website traffic, or sensor readings where you only care about what’s happening right now.
Best for: Real-time monitoring, alerts, or dashboards where speed matters more than storage.
3. PubNub Streaming Datasets
For high-frequency, large-scale, real-time streaming, Power BI PubNub integration works well.
PubNub is a global data-streaming service. This setup delivers data instantly and reliably, even when thousands of devices or applications are sending updates at once.
Example: PubNub streaming database is best for IoT environments where multiple factory sensors continuously transmit readings like temperature, pressure, or vibration data.
Best for: Large-scale IoT and connected-device scenarios needing sub-second updates and dependable global performance.
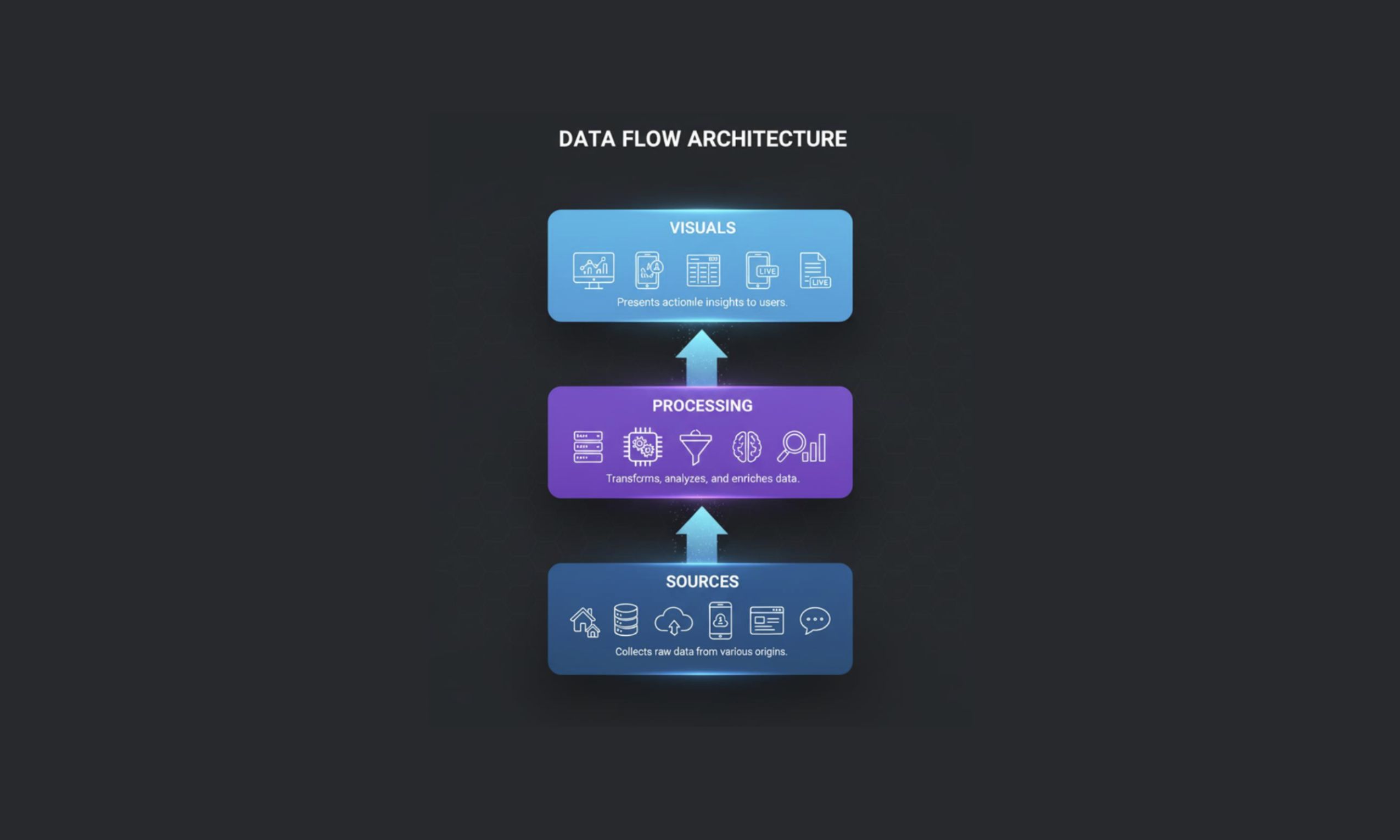
The architecture behind Streaming Data in Power BI
Behind every live dashboard in Power BI is a tightly integrated architecture designed to capture, process, and display data in near real time — often within seconds of it being generated. It’s what turns data streams into live insights with almost zero lag.
Here’s how you can turn any streaming data sets into real-time Power BI dashboards.
Connect data sources
Streaming starts at the source. This could be anything that generates continuous data:
IoT sensors on a manufacturing floor,
APIs sending live metrics from web or mobile apps,
Cloud services like Azure IoT Hub or Event Hub,
Or even enterprise systems pushing updates through connectors.
These data points flow continuously, forming the raw input that Power BI can consume.
The real-time engine - Power BI Service
Power BI service is the backbone of the entire pipeline, making real-time data ingestion and processing happen — ensuring that every new data point triggers an instant visual update without requiring a manual refresh.
Once the data reaches Power BI Service, it’s immediately ingested and streamed to connected dashboards and reports.
Users can configure three types of real-time datasets — Push, Streaming, or PubNub — depending on whether they need historical storage, purely live visuals, or large-scale global streaming.
Azure Stream Analytics
For scenarios where the raw data needs cleaning, enrichment, or complex processing before it hits Power BI, Azure Stream Analytics (ASA) can be an optional yet powerful middle layer for real-time processing.
Here is what Azure Streaming analytics can do:
Aggregating multiple event streams,
Filtering noise or anomalies,
Detecting patterns and correlations across time windows,
And preparing the data for immediate visualization.
ASA then pushes the processed stream into Power BI for live reporting.
Think of it as your real-time ETL engine, transforming streams on the fly.
Data hits the visualization layer
Finally, the live data reaches Power BI — updating visuals into dashboard segments like cards, gauges, charts, and stamps the moment. This layer enables teams to act on the latest metrics instantly — whether it’s monitoring equipment health, website traffic, or market fluctuations.
You can build dashboards that refresh every second, enabling instant feedback loops across departments.
Use cases of Streaming data in Power BI
Business Scenario | Streaming Dataset Type | Why It Fits Best |
|---|---|---|
Website analytics | Streaming Dataset | Focus on current sessions and visitor clicks in real time |
IoT Monitoring | Push Dataset | Need both immediate updates and historical performance tracking |
Social Media Engagement | PubNub Dataset | Handles high-frequency global message stream |
Sales & Inventory | Push Dataset | Historical storage supports forecasting and trend analysis |
Security Alerts | Streaming Dataset | Provides instant alerts for anomalies or breaches |
Where streaming data falls short
There are some limitations one may face while handling streaming datasets.
Data Retention: Streaming datasets without storage can only display data temporarily.
Licensing: Some streaming options require Power BI Pro or Premium capacities.
Performance: High-volume streams may need careful management of refresh rates and data filters.
Complex Transformations: Advanced data modeling or computations might need Azure Stream Analytics or Power Query integration.
Final thoughts
Having the capability to deal with continuous data is being able to see tomorrow and act ahead. Any company that has already invested in or thinking about Microsoft ecosystem, can utilize Power BI’s streaming capabilities and build a robust and scalable solution for unlocking the value of live data.
Because it’s not just about analytics anymore—it’s about responding, adapting, and thriving in an ever-changing environment.
Let’s help you shift from “What happened yesterday?” to “What is happening right now, and how should we respond?”

by Kannabiran
Kannabiran, a senior and Lead Data Engineer at datakulture, has led the strategy and delivery of cost-effective, efficient data infrastructures for companies across industries. A strong advocate of metadata-driven architecture, he brings deep knowledge of modern data engineering concepts and tools, and actively shares this expertise through blogs, videos, and community conversations. He is also the driving force behind building our novel ETL framework, while also guiding and nurturing young data engineers and interns.